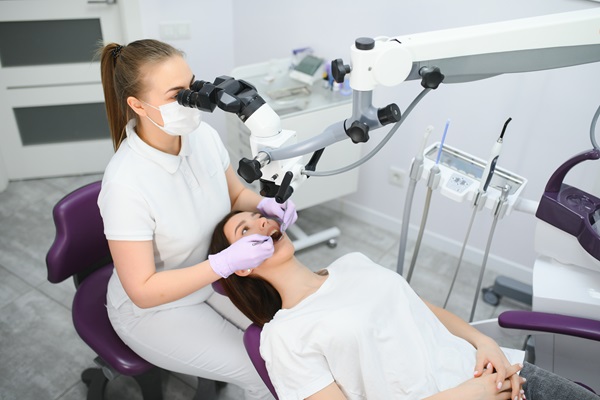
Oral surgery is a broad term that covers a wide variety of procedures related to teeth and gums. There are a number of reasons dentists may recommend dental surgery for a patient. Most often, they do so if the pain or discomfort a patient is feeling or an injury or infection goes deep enough into the tooth or jaw that it requires more invasive treatments.
Situations when dental surgery may be recommended
Certain oral health problems make it more likely for a dentist to recommend the patient receive oral surgery.
Impacted teeth
Most often occurring when a patient's wisdom teeth start to grow in, impacted teeth are the result of the jaw being too small to fit all of the patient's permanent teeth into the mouth comfortably. The crowding makes it so that the teeth do not come out of the gums completely, in turn causing soreness and possibly even infections. Without surgery to remove the impacted teeth, impactions can also lead to permanent damage to other teeth, the gums, or the bones in the jaw.
Dental implants
When people have broken or missing teeth, they often choose to replace them with bridges or dentures. Typically, a general dentist performs these procedures. However, some patients prefer a more permanent solution in the form of dental implants. The process requires the implantation of titanium rods into the gums in a surgical procedure. Replacement crowns are then attached to the implants. Dental implants not only look almost indistinguishable from the original teeth but also are as functional.
Overbites or underbites
Many people have misaligned teeth in the form of overbites or underbites, but sometimes the misalignment is too severe for standard orthodontic treatments. Excessive overbites or underbites can lead to trouble chewing and swallowing food, sleep apnea, difficulty speaking, and even trouble breathing. While braces can often fix these problems, sometimes they cannot sufficiently reposition the jaw. More severe cases often require oral surgery that involves moving all or part of the jaw into a new position. Once healed, the patient has a more functional and healthy mouth.
Issues with the joint in the jaw
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects the jaw to the skull. Problems with the "hinge" right in front of the ears can cause popping, headaches, stiffness, and pain. Those who have TMJ disorders usually start a course of treatment that includes oral medication and physical therapy. However, cases sometimes advance and become a specific problem that can only be fixed by surgery.
Cancer treatments
Patients who have oral cancer or cancer of the sinuses, throat, lips, larynx, or salivary glands often require surgery to remove cancerous cells or masses. From there, they usually receive radiation or chemotherapy to go into remission.
Conclusion
While your dentist can help you with many oral health ailments, it is important to follow any advice if oral surgery is recommended. Appropriate surgical procedures help to ensure you heal smoothly and retain function of your teeth and jaw.
Request an appointment here: https://brookemcloningerdds.com or call Brooke M. Cloninger, D.D.S. at (509) 319-2152 for an appointment in our Spokane office.
Related Posts
Can a General Dentist Perform Oral Surgery?
The idea of oral surgery can be intimidating, especially when your dentist recommends it. It is easy to understand the extra layer of anxiety that happens when the dentist goes on to …
Aftercare for In Office Professional Dental Cleaning
An in-office professional dental cleaning is a crucial aspect of maintaining good oral health. While oral hygiene done at home is a great way to keep the teeth and gums healthy, it …
What Is a Preventative Dentist?
A preventative dentist focuses on maintaining a patient’s oral health and preventing problems, such as sensitive teeth, from becoming more serious issues, like gum disease. This typically involves routine dental checkups, cleanings, …
Metal Crowns vs. Porcelain Dental Crowns
Dental crowns can treat many different concerns. They can repair damaged teeth, attach to dental implants for teeth replacement, and more. Two of the main types of dental crowns are metal and …